AWS Learning notes
Learning notes for the AWS Certified Solutions Architect - Associate exam
Published: Tuesday, Jun 27, 2023 Last modified: Sunday, May 19, 2024
RDS Proxy
RDS Proxy establishes and manages the necessary connection pools to your database so that your application creates fewer database connections.
https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/compute/using-amazon-rds-proxy-with-aws-lambda/
AWS Backup
In AWS Backup, a backup vault is a container that stores and organizes your backups.
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/aws-backup/latest/devguide/vaults.html
AWS DataSync (AMS SSPS)
AWS DataSync moves large amounts of data online between on-premises storage and Amazon S3, Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon Elastic File System) or Amazon FSx.
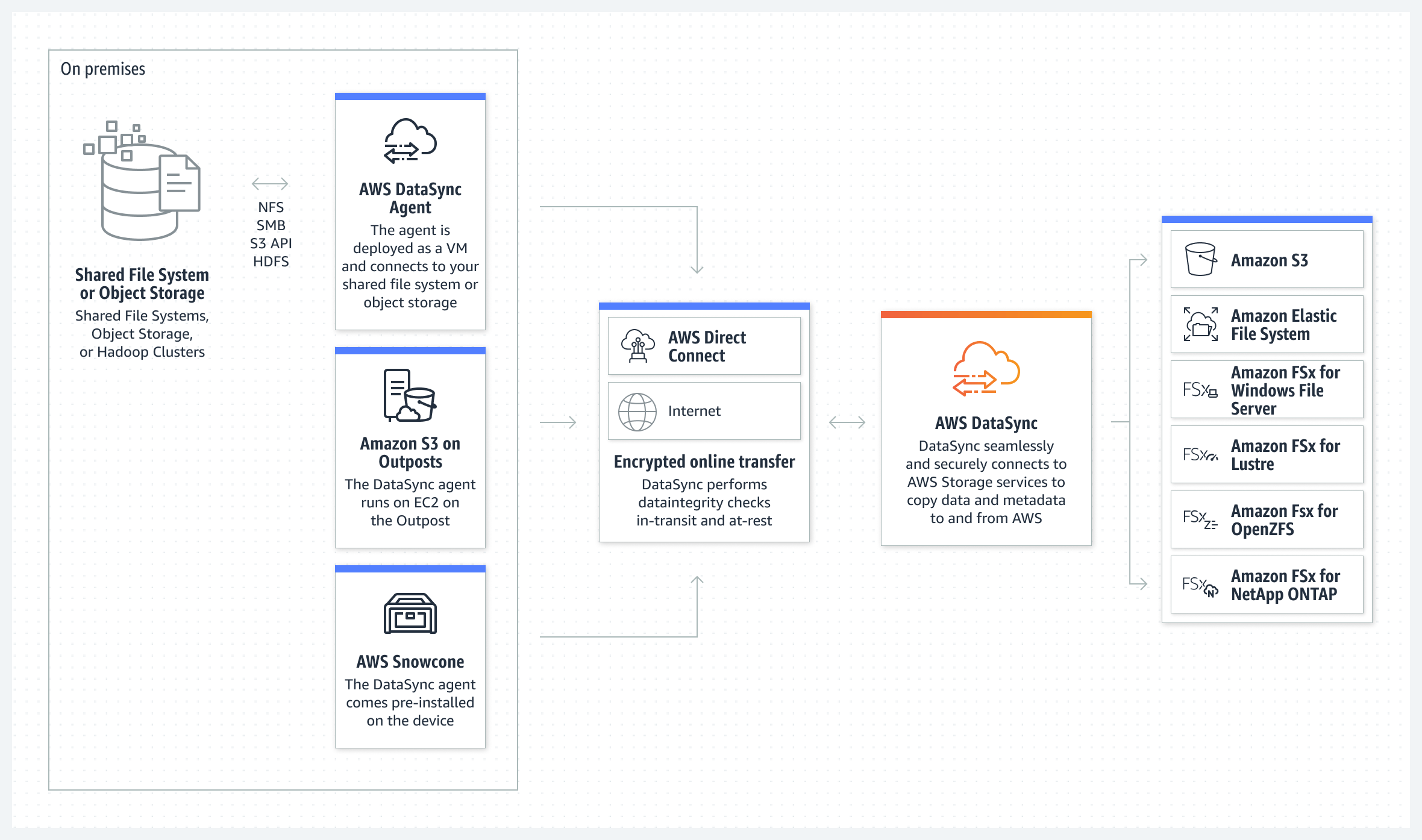
DataSync software agent connects to your Network File System (NFS) and Server Message Block (SMB) storage, so you don’t have to modify your applications
Deny access based on source IP address “NotIpAddress”
Comes under AWS global condition context keys.
Be careful using negative conditions in the same policy statement as “Effect”: “Deny”. When you do, the actions specified in the policy statement are explicitly denied in all conditions except for the ones specified.
Amazon Aurora Global Database
- RPO is < 1 second
- RTO is one minute
Amazon Aurora Global Database is designed for globally distributed applications, allowing a single Amazon Aurora database to span multiple AWS Regions. It replicates your data with no impact on database performance, enables fast local reads with low latency in each Region, and provides disaster recovery from Region-wide outages.
https://aws.amazon.com/rds/aurora/global-database/
Lambda
Offers resource-based policies
Lambda supports resource-based permissions policies for Lambda functions and layers. Resource-based policies let you grant usage permission to other AWS accounts or organizations on a per-resource basis. You also use a resource-based policy to allow an AWS service to invoke your function on your behalf.
Amazon FSx for Lustre
- High performance
- Fast processing
- Parallel filesystem
AWS S3 Compliance types
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/userguide/object-lock-overview.html
S3 Object Lock provides two retention modes:
- Governance mode - users can’t overwrite or delete an object version or alter its lock settings unless they have special permissions;
x-amz-bypass-governance-retention:trueheader and s3:BypassGovernanceRetention - Compliance mode
In compliance mode, a protected object version can’t be overwritten or deleted by any user, including the root user in your AWS account. When an object is locked in compliance mode, its retention mode can’t be changed, and its retention period can’t be shortened. Compliance mode helps ensure that an object version can’t be overwritten or deleted for the duration of the retention period.
AWS billing sharing discounts
S3 Replication reasons
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/userguide/replication.html#crr-scenario
Governance
What do you use to restrict a set of account to certain AWS services or a service with say certain EC2 types?
- Service control policies (SCPs) - no, this disables the entire service, e.g. no usage of EC2 at all
- https://aws.amazon.com/proton/ - enforce standards, e.g. path to production / deployment aimed at microservice workloads
- AWS Service Catalog - this is for a superset including how to provision databases and groups of services
- IAM policy - yes
Notes
Security Groups are on the instance level, not the subnet level.
AWS S3 Glacier instant retrieval for rare cases.
AWS Guard Duty offers continuous monitoring.
Backup + Restore strategy is the cheapest backup strategy. Next level is Pilot Light.

SQS not guaranteed to preserve order by default. Kinesis preserves ordering.
WAF is for Layer 7, AWS Network Firewall provides “control and visibility to Layer 3-7 network traffic for your entire VPC”.
Managing cross account resources? You need:
- Organisations
- AWS RAM
AWS Volume Gateway = SCSI
Compliance = AWS Artifact
Cloudwatch Events = Amazon Eventbridge
EC2 Health Check fail should mean a reboot (that also keeps the resources in tact)
EC2 stopped = resources reallocated
Firewall manager to centrally manage rules
AWS Shield (by default), AWS Shield Advanced = Extra