Published: Thursday, Jul 28, 2016 Last modified: Wednesday, Feb 4, 2026
Following up after [[ECS_questions]]
docker-compose.yml example
version: '2'
services:
web:
image: kaihendry/count
ports:
- "80:8080"
mem_limit: 1043333120
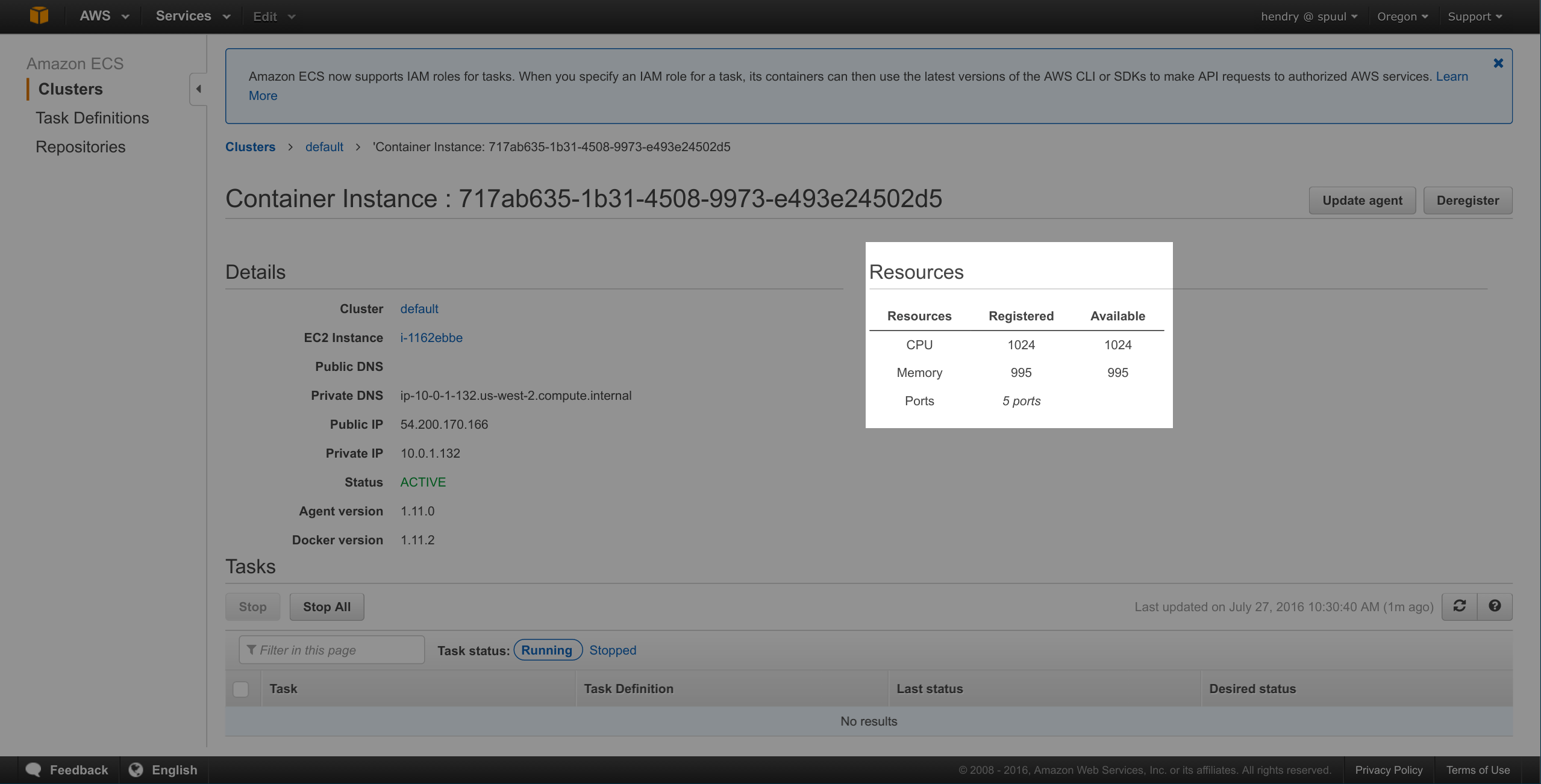
Mem limit was figured by taking Available Memory, t2.micro is 995 and getting bytes like so:
~$ echo $((995 << 20))
1043333120
Assuming you have the docker-compose.yml ready and ecs-cli configured,
start up the cluster of a EC2 instance running the service like so:
ecs-cli up --capability-iam --keypair example_sysadmin
ecs-cli compose service ps
Setting up the load balancer is manual
Create the service by attaching the load balancer to the task
export CLUSTER_NAME=default
aws --region ap-southeast-1 ecs create-service --service-name "ecscompose-service-count" \
--cluster "$CLUSTER_NAME" \
--task-definition "ecscompose-count" \
--load-balancers "loadBalancerName=ecs-count,containerName=web,containerPort=9000" \
--desired-count 1 --deployment-configuration "maximumPercent=100,minimumHealthyPercent=50" --role ecsServiceRole
- Make it’s in the VPC of the created ECS (look at tags)
- Make sure the security groups are permissive
- Make sure the health check is /, not
/index.html - Setup Route 53 to point to ELB (e.g. ecs.example.com)
- Website requires SSL
- You do not need to setup ELB in the service, in fact it’s a lot easier if you don’t since it gets confused by port re-mappings.
Caveats
ecs-cli down will not work until you remove the ELB
https://console.aws.amazon.com/support/home?region=us-west-2#/case/?displayId=1820472381&language=en.
So you need to terminate the instance manually if you want to save some money.
ecs-cli up by default will create a security group that you can’t ssh into.
Developer workflow
aws ecr get-login --profile example --region us-west-2
docker build -t website .
docker tag website:latest 111111111.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/website:latest
docker push 111111111.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/website:latest
Typically a 100mb upload
Then bring down the service and up the service like so: http://s.natalian.org/2016-07-27/ecs.txt
Bringing down a service
ecs-cli compose service down
Will bring down the particular service. Note that it’s conceivable that many services run on an instance.
You can kill the entire cluster like ecs-cli down --force, but I don’t
recommend that because the VPC will change when you re-establish it, so your
previously manually set up load balancer will not work.
Current workaround is to manually terminal the EC2 instance from the Web console if I am not requiring it.
DNS failover
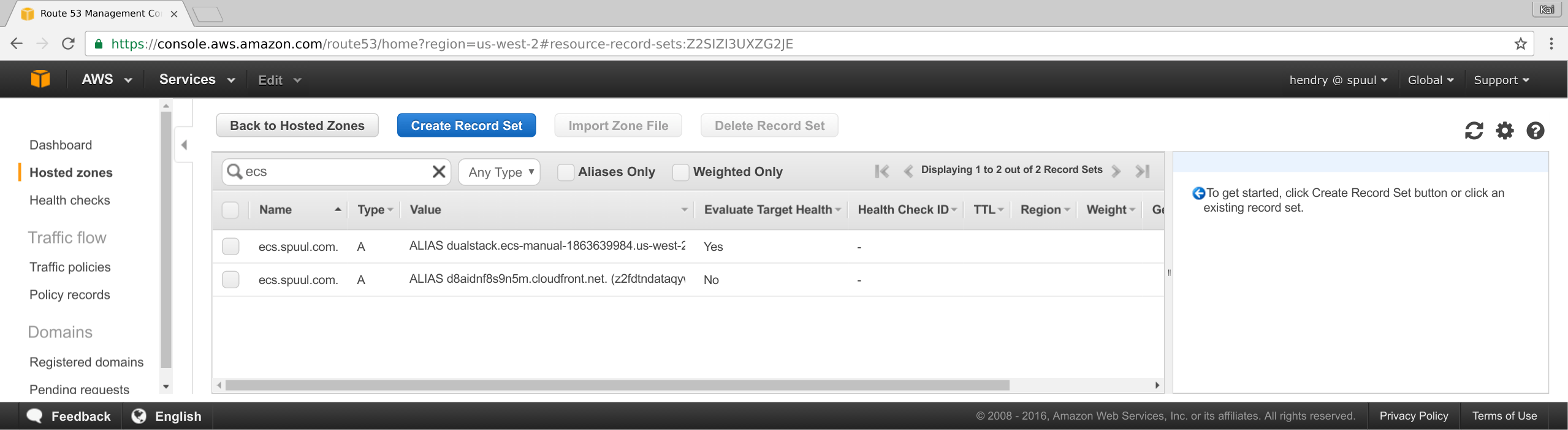
Notice that “Evaluate Target Health” is enough for the Failover rule to know the load balancer is out of action. You do not need a health check!
We fail over to Cloudfront since we require SSL to work.
Upgrade flow
Upgrading the container image
Running two instances with the container running on each and then doing a
ecs-cli compose service up should upgrade the service I’m told, but I doubt
it works. Some careful orchestration with Health limits.
Upgrading the EC2 instance image
Upgrading an instance basically means killing it and starting it again. I guess that would entail a scale event to launch a new instance. ssh to it to ensure it’s uptodate (security group permitting). And then decommission the old one by removing it from the load balancer.
Issues
No way to terminate last EC2 Instance in cluster:
$ ecs-cli scale --size 0 --capability-iam
INFO[0002] Waiting for your cluster resources to be updated
INFO[0003] Cloudformation stack status stackStatus=UPDATE_IN_PROGRESS
ERRO[0035] Failure event reason= resourceType=AWS::CloudFormation::Stack
ERRO[0035] Error executing 'scale': Cloudformation failure waiting for 'UPDATE_COMPLETE'. State is 'UPDATE_ROLLBACK_COMPLETE'
Steps
ecs-cli up --capability-iam --keypair spuul_sysadminecs-cli compose service upto create service- Find VPC name http://s.natalian.org/2016-08-02/1470124829_2558x1404.png
- Create service from task and associate ELB
- Update Route 53 Failover record with ELB name in case things really go badly